

If a device that belongs to a supported device class is connected to a system, Windows automatically loads the class driver, and the device functions with no additional driver required. Microsoft provides in-box drivers for several of those device classes, called USB device class drivers. Each device class is identified by USB-IF approved class, subclass, and protocol codes, all of which are provided by the IHV in device descriptors in the firmware. Those classes and their specifications are defined by the USB-IF. USB Device classes are categories of devices with similar characteristics and that perform common functions. More guidelines are included in Choosing a driver model for developing a USB client driver. If a Microsoft-provided driver is not available for the USB device class to which your device belongs, then consider using generic drivers, Winusb.sys or Usbccgp.sys. If you are writing a custom driver: Before writing a driver for your USB device, determine whether a Microsoft-provided driver meets the device requirements. The drivers are updated through Windows Update. They are available in the \Windows\System32\DriverStore\FileRepository folder. These drivers and their installation files are included in Windows. If you are installing USB drivers: You do not need to download USB device class drivers. For non-composite devices or a function of a composite device, use WinUSB (Winusb.sys).
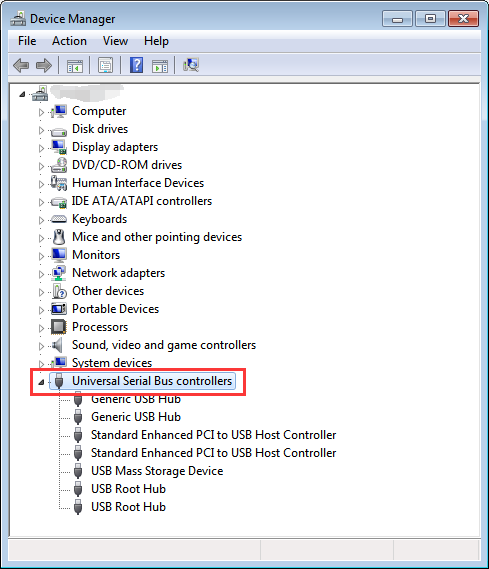

By clicking at the targeted laptop model, you’ll be able to look through a comprehensive list of compatible devices.This topic is for programmers. We have compiled a list of popular laptops models applicable for the installation of ‘USB Mass Storage Device’. USB Mass Storage Device: Supported Models of Laptops


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
